How To Make A Joint Probability Table
What is a Joint Probability?
A articulation probability, in probability theory, refers to the probability that two events will both occur. In other words, joint probability is the likelihood of two events occurring together.

Formula for Joint Probability
![]()
Where:
- P(A ⋂ B) is the notation for the articulation probability of issue "A" and "B".
- P(A) is the probability of event "A" occurring.
- P(B) is the probability of event "B" occurring.
Joint Probability and Independence
For joint probability calculations to piece of work, the events must exist independent. In other words, the events must not exist able to influence each other. To determine whether two events are independent or dependent, it is important to ask whether the consequence of i result would take an impact on the outcome of the other upshot. If the outcome of one consequence does non affect the event of the other outcome, the events are independent.
An instance of dependent events is the probability of the clouds in the heaven and the probability of rain on that mean solar day. The probability of clouds in the sky has an affect on the probability of rain that day. They are, therefore, dependent events.
An example of independent events is the probability of getting heads on two coin tosses. The probability of getting a head on the outset coin toss does not have an touch on the probability of getting heads on the second coin toss.
Visual Representation
A articulation probability can exist visually represented through a Venn diagram. Consider the articulation probability of rolling two 6's in a fair six-sided dice:
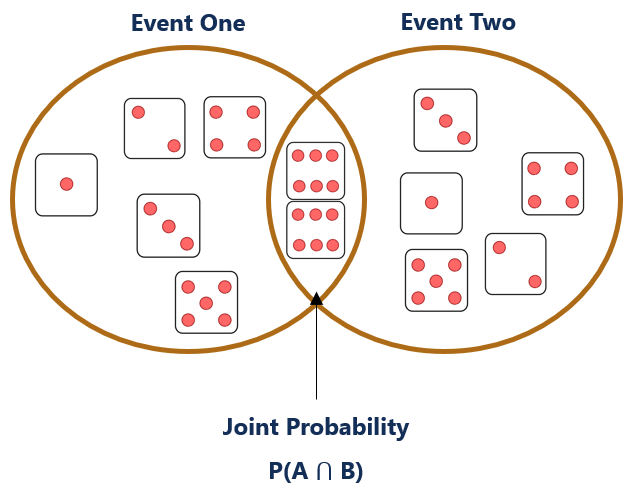
Shown on the Venn diagram in a higher place, the joint probability is where both circles overlap each other. It is called the "intersection of 2 events."
Examples
The following are examples of joint probability:
Case 1
What is the joint probability of rolling the number five twice in a fair six-sided dice?
Event "A" = The probability of rolling a 5 in the get-go roll is 1/vi = 0.1666.
Consequence "B" = The probability of rolling a 5 in the 2nd curl is 1/6 = 0.1666.
Therefore, the joint probability of consequence "A" and "B" is P(i/6) x P(1/6) = 0.02777 = 2.eight%.
Example 2
What is the joint probability of getting a head followed by a tail in a coin toss?
Event "A" = The probability of getting a head in the first money toss is i/2 = 0.five.
Effect "B" = The probability of getting a tail in the second coin toss is ane/ii = 0.five.
Therefore, the joint probability of event "A" and "B" is P(1/ii) x P(1/2) = 0.25 = 25%.
Case three
What is the joint probability of drawing a number 10 carte that is black?
Event "A" = The probability of drawing a ten = four/52 = 0.0769
Event "B" = The probability of cartoon a blackness carte du jour = 26/52 = 0.50
Therefore, the articulation probability of event "A" and "B" is P(4/52) 10 P(26/52) = 0.0385 = 3.nine%.
More Resources
CFI is the official provider of the global Fiscal Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ certification programme, designed to help anyone go a earth-course financial analyst. To keep learning and advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
- Basic Statistics Concepts in Finance
- Empirical Probability
- Normal Distribution
- Subjective Probability
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/other/joint-probability/
Posted by: hestertoeopla.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Make A Joint Probability Table"
Post a Comment